How to Prepare for Economic Consultancy Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
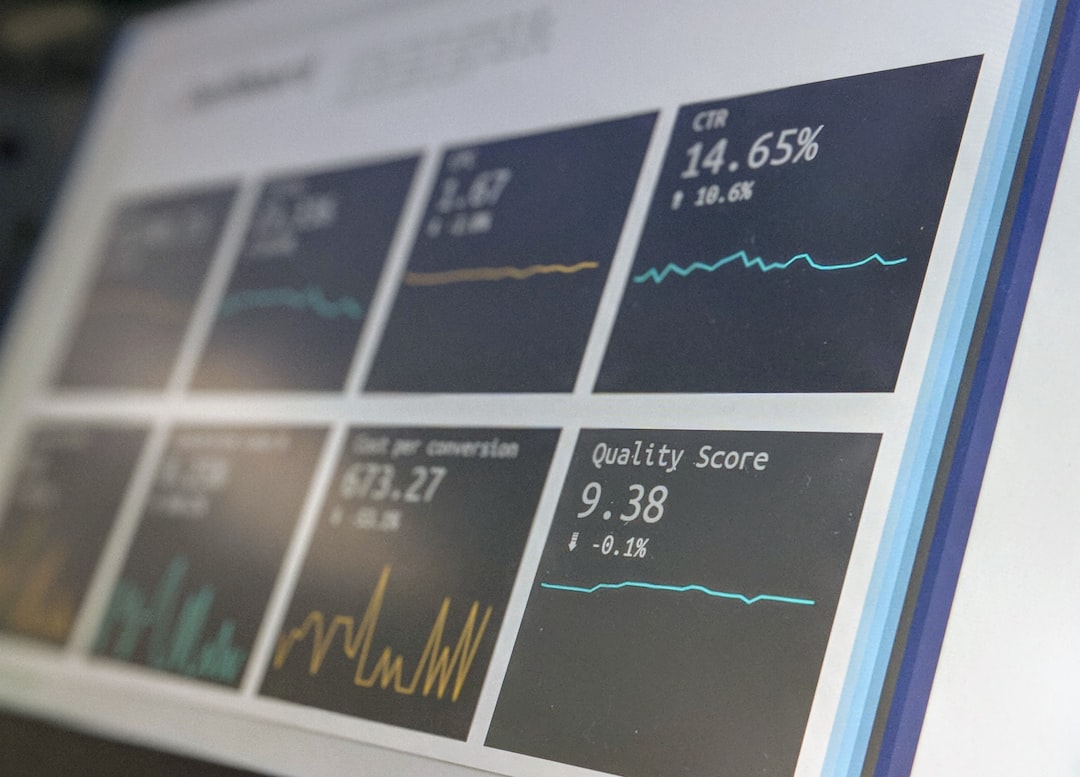
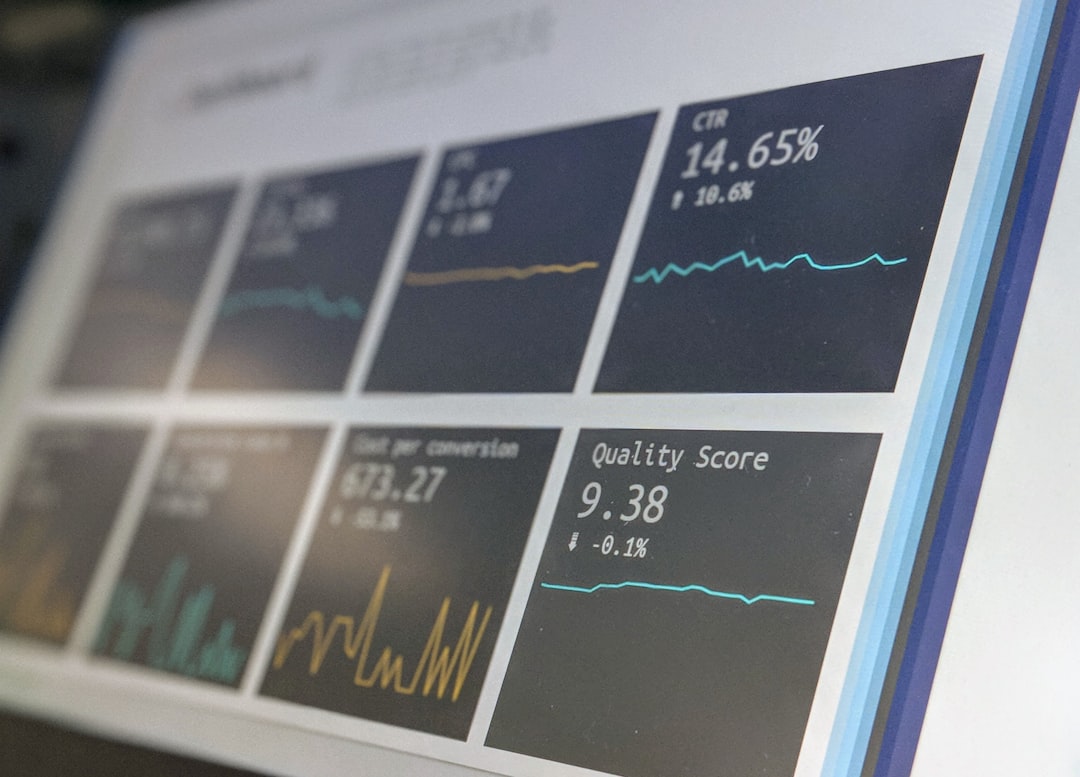
# Introduction. Embarking on an economic consultancy project can be both thrilling and daunting. With a plethora of elements to consider, the path to impactful outcomes often requires careful preparation. Whether you are a seasoned consultant or venturing into this field for the first time, understanding the nuances of economic consultancy can enhance your effectiveness and the value you provide to clients. This guide will traverse the vital steps to adequately prepare for economic consultancy projects, ensuring that you can navigate challenges and seize opportunities effectively. # Understanding the Project Scope and Objectives. Before diving into any consultancy project, it is essential to clarify its scope and objectives. Start by engaging with your clients to understand their specific needs and expectations. Ask probing questions about their goals, timelines, and key performance indicators. - **Define Objectives Clearly**: Ensure that both you and your client share a unified vision regarding the project’s intended outcomes. This clarity allows for better focus during the project and serves as a benchmark against which progress can be measured. - **Establish a Work Breakdown Structure**: Draft a work breakdown structure (WBS) to detail the tasks needed to meet the project’s objectives. This blueprint will serve as a roadmap to guide your activities and help allocate resources efficiently. # Conducting Thorough Research and Analysis. A successful economic consultancy project is grounded in robust research and analysis. The following strategies can enhance your research efforts: - **Gather Relevant Data**: Utilize credible sources such as government databases, academic journals, and industry reports to compile data that supports your analysis. This foundational information is crucial for understanding the economic environment surrounding your project. - **Employ Analytical Frameworks**: Leverage economic theories and analytical frameworks such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis, PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) analysis, or Porter's Five Forces to create insights. - **Consult Subject Matter Experts**: When necessary, consult with subject matter experts who have deep knowledge in the specific area your project encompasses. Their insights can provide invaluable context and validation for your findings. # Developing a Strategic Plan. Once you have gathered and analyzed your data, it’s time to formulate a strategic plan to present your recommendations. Here are some key components to include: - **Set Clear Deliverables**: Outline tangible deliverables that describe what clients can expect from your consultancy. This minimizes misunderstandings and establishes benchmarks for success. - **Rank Recommendations by Impact**: Prioritize your recommendations based on their potential impact and feasibility. This structured approach helps clients focus on high-impact strategies first, leading to swift results. - **Consider Risk Management**: Identify potential risks associated with your recommendations and develop contingency plans to address these challenges. This proactive approach builds trust and shows your commitment to successful outcomes. # Enhancing Communication Skills. In economic consultancy, your ability to communicate effectively can significantly influence the success of your project. Here are ways to enhance your communication: - **Tailor Your Message**: Adapt your communication style to match your audience’s preferences and knowledge level. This might involve simplifying complex economic jargon for non-economists yet presenting detailed analytics for stakeholders familiar with economic principles. - **Utilize Visual Aids**: Incorporating charts, graphs, and infographics can make your findings more accessible and engaging. Visual storytelling can drive your points home more effectively than dense text. - **Practice Active Listening**: Ensure that you’re not just presenting information but also engaging with clients by actively listening to their feedback and concerns. This reciprocity fosters collaboration and leads to more tailored recommendations. # Staying Up-to-Date with Economic Trends. The field of economics is ever-evolving, making it crucial to stay informed about current trends and issues impacting the economy. Here’s how: - **Follow Economic News**: Regularly read reputable economic news sources such as The Economist, Financial Times, or Bloomberg to stay in the loop about global and regional economic developments. - **Engage in Continuing Education**: Pursuing additional certifications, attending workshops, or enrolling in relevant courses can enhance your knowledge base and set you apart in the consultancy field. - **Join Professional Networks**: Becoming part of economic and business associations allows you to interact with peers and industry leaders. Networking can facilitate sharing insights and best practices while also keeping you informed. # Conclusion. As the landscape of economic consultancy continues to grow in complexity, ensuring thorough preparation is paramount. From understanding project scope to conducting meticulous research and fostering effective communication, each step contributes to your overall efficacy as an economic consultant. By adopting a structured approach and continuously updating your knowledge, you can position yourself as a valuable asset to your clients. In the ever-changing world of economics, being prepared will empower you to navigate challenges and deliver insightful, impactful consultancy services. .