The Economist’s Guide to Data Collection: Strategies for Effectiveness
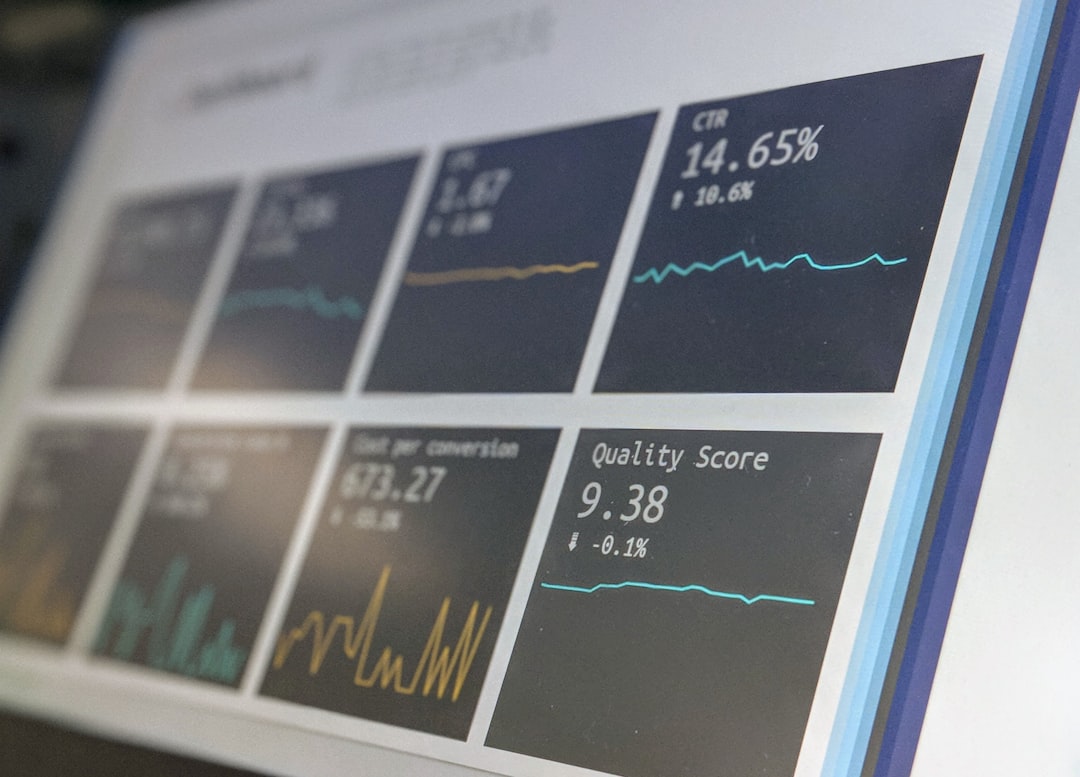
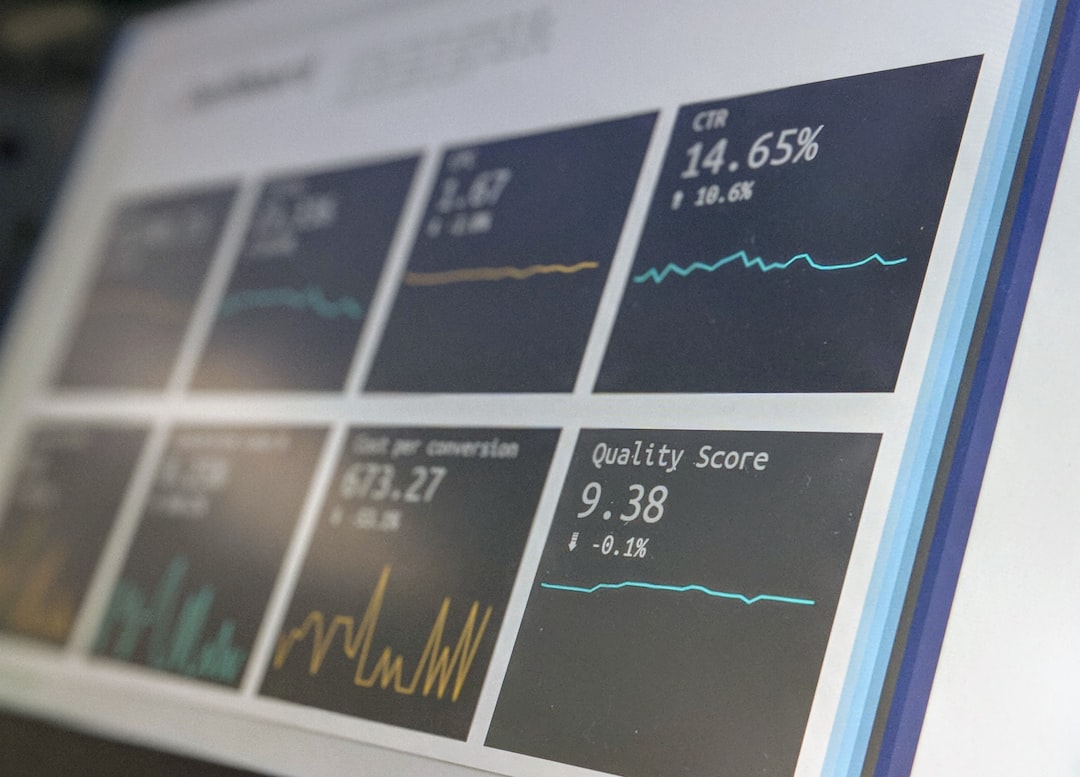
# Introduction. Data collection is a critical component of economic analysis, business strategy, and policy formulation. The effectiveness of any research or analysis is largely dependent on the quality and reliability of the data collected. As organizations navigate a more data-driven environment, a structured approach to data collection becomes essential. This guide by The Economist explores best practices, methodologies, and tools necessary for effective data collection. # Understanding Data Collection Methods. Data collection can be classified into primary and secondary methods. Primary data collection involves gathering new data directly from the source, often through surveys, interviews, or observations. This method allows researchers to collect specific information tailored to their study’s goals. In contrast, secondary data collection involves using existing data that has already been gathered by other sources, such as government statistics or academic research. Understanding when to use each method is crucial. For example, if you're exploring new consumer preferences, primary data may provide the freshest insights. Conversely, secondary data could prove invaluable when analyzing industry trends or historical data. # Tools for Data Collection. In an age of technological advancements, various tools can facilitate data collection. Online survey platforms, like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey, allow researchers to design custom surveys and reach respondents easily. Data management software can help store, analyze, and visualize collected data seamlessly. Additionally, mobile applications can enable data collection on the go, making it easier to gather fresh insights from real-time interactions. These tools also often offer built-in analytics features, helping to interpret results efficiently. # Ensuring Data Quality and Reliability. Data quality is paramount in any research study. Inaccurate data can lead to erroneous conclusions, impacting decision-making. Several best practices can enhance data reliability: firstly, clearly define what data you need and why; secondly, make sure to train staff thoroughly in data collection methods; and lastly, implement a system of checks and validations throughout the collection process. For example, double-checking survey responses or implementing cross-verification techniques can help identify discrepancies early. Having these measures in place not only fosters confidence in the data but also strengthens the overall quality of the research project. # Ethical Considerations in Data Collection. With the rise of data privacy concerns, emphasizing ethical considerations in data collection is crucial. Researchers must always obtain informed consent from participants, clearly outlining how their data will be used. Privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, underscore the importance of protecting personal information. Data anonymization techniques can help safeguard identities while still allowing researchers to extract meaningful insights from the data. Ensuring compliance with ethical standards is not only a legal obligation but also essential for maintaining public trust. # Analyzing and Interpreting Collected Data. Once data has been collected, the next step is analysis. Choosing the right analytical methods will depend on the research objectives and the nature of the data. Statistical tools, such as regression analysis or variance analysis, can help identify trends, correlations, or cause-effect relationships. Visualization tools, like charts and graphs, can simplify the interpretation of complex data sets, making the results easier to comprehend. Ultimately, clear communication of findings is necessary to inform stakeholders effectively. # Conclusion. Effective data collection is a multi-faceted process that requires careful planning, execution, and ethical consideration. By understanding various data collection methods, utilizing appropriate tools, ensuring data quality, and adhering to ethical guidelines, organizations can develop a robust framework for data collection. This guide serves as a stepping stone toward implementing and refining successful data collection strategies that align with organizational goals and foster informed decision-making. # Images Search Tags. Data collection tools and methods for research. .