How to Analyze Financial Statements for Economic Research
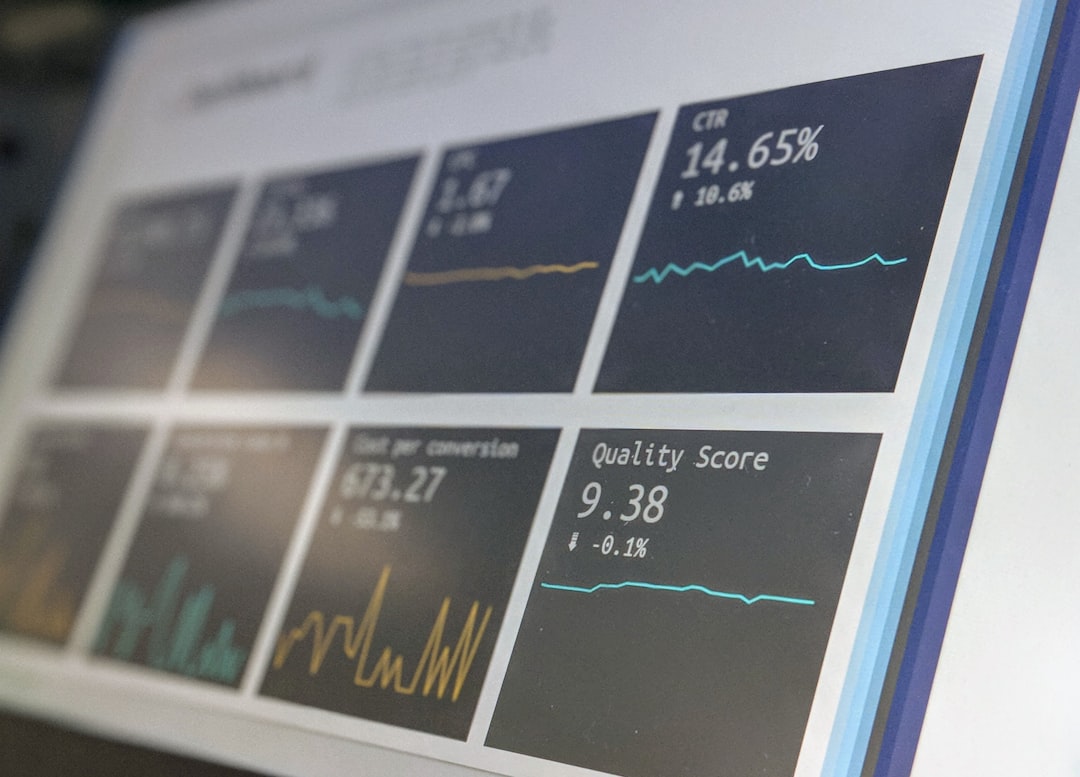
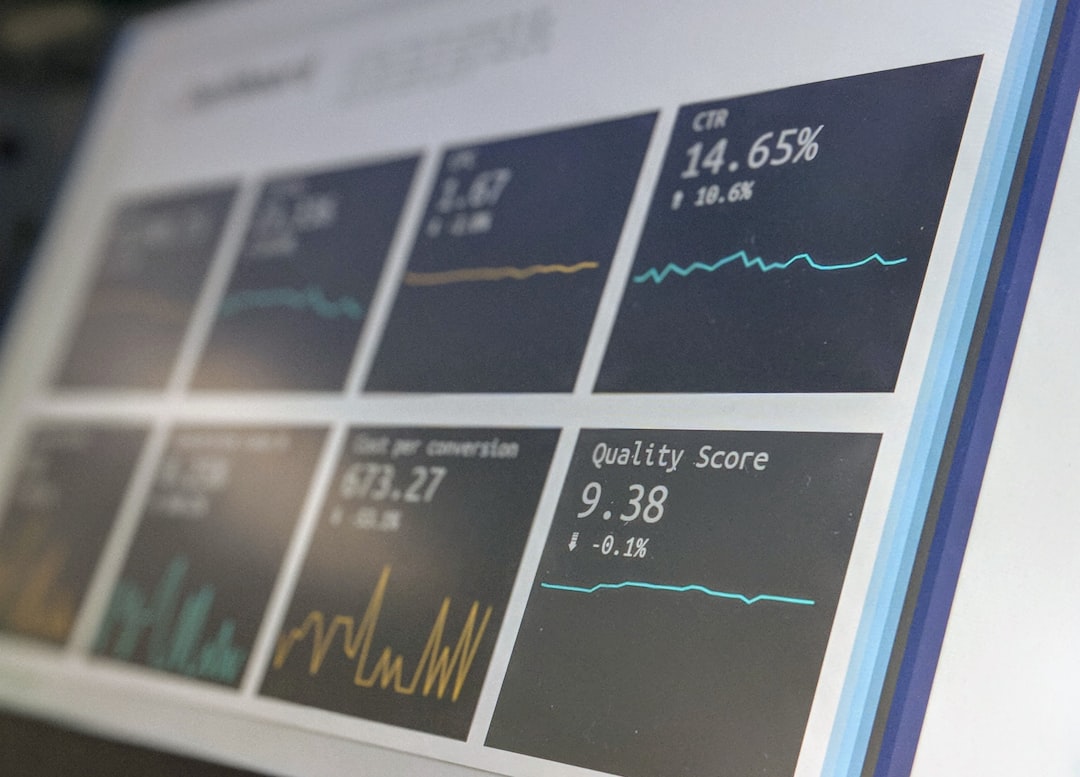
# Introduction. Analyzing financial statements is a critical skill for anyone involved in economic research, whether in academia, investment, or consulting. Financial statements provide a wealth of information about a company’s performance and can illuminate trends and issues within the broader economy. By understanding these statements, researchers can derive insights into market dynamics, assess the financial health of companies, and predict future economic conditions. This post will guide you through the process of analyzing financial statements and highlight key areas to focus on. # Understanding Financial Statements. Before diving into the analysis, it is essential to understand the three primary types of financial statements: the Balance Sheet, the Income Statement, and the Cash Flow Statement. ## Balance Sheet. The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Key components include: - **Assets**: What the company owns (cash, inventory, properties). - **Liabilities**: What the company owes (loans, accounts payable). - **Equity**: The residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities. A strong balance sheet often indicates a financially healthy company. Pay attention to the debt-to-equity ratio to understand how leveraged the company is. ## Income Statement. The Income Statement shows the company’s revenues and expenses over a period, typically a quarter or a year. Components include: - **Revenue**: The total income generated from sales. - **Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)**: Direct costs attributable to the production of goods. - **Net Income**: The profit after all expenses. Analyzing trends in revenue and expenses can help researchers gauge a company's profitability and operational efficiency. ## Cash Flow Statement. The Cash Flow Statement outlines how cash flows in and out of a business, categorized into three areas: operating, investing, and financing. - **Operating Activities**: Cash generated or spent on daily operational activities. - **Investing Activities**: Cash flows related to buying and selling assets. - **Financing Activities**: Cash flows from issuing stock or debt repayment. Analyzing cash flows can reveal how well a company manages its liquidity, which is crucial for sustaining operations. # Key Ratios for Analysis. Once you are familiar with the financial statements, calculating key financial ratios can provide deeper insights into a company's performance. Here are some important ratios: ## Profitability Ratios. These ratios, such as Gross Profit Margin and Net Profit Margin, help assess how well a company generates profit relative to its revenue or sales. ## Liquidity Ratios. The current ratio and quick ratio are critical to determining a company's ability to cover its short-term obligations. A current ratio of 1 or higher is generally considered a good indicator of liquidity. ## Leverage Ratios. Ratios like the Debt-to-Equity ratio measure the degree to which a company is financing its operations through debt. High leverage can indicate higher risk, particularly in volatile economies. # Qualitative Factors in Financial Analysis. While quantitative analysis is vital, qualitative factors also play a crucial role in financial analysis. For instance, management effectiveness, market competition, and regulatory environment must be considered. Companies with strong leadership and a clear strategy are often better positioned to navigate challenges. # Contextual Analysis in Economic Research. When analyzing financial statements for economic research, context is vital. Compare the company’s performance to industry benchmarks and economic indicators. Additionally, consider macroeconomic factors such as inflation rates, unemployment, and GDP growth that can significantly influence company performance. Tools like SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis can provide further understanding of a company’s standing within its industry. # Conclusion. Analyzing financial statements is a powerful tool for economic research, enabling you to understand the financial health of companies and their implications for the broader economy. By mastering the basics of financial statements, ratios, and qualitative factors, researchers can extract meaningful insights that drive strategic decision-making, forecasting, and tender financial analyses. In today’s complex economic landscape, this skill has never been more crucial. .