Economic Predictions for 2023 and Beyond: Navigating the Future
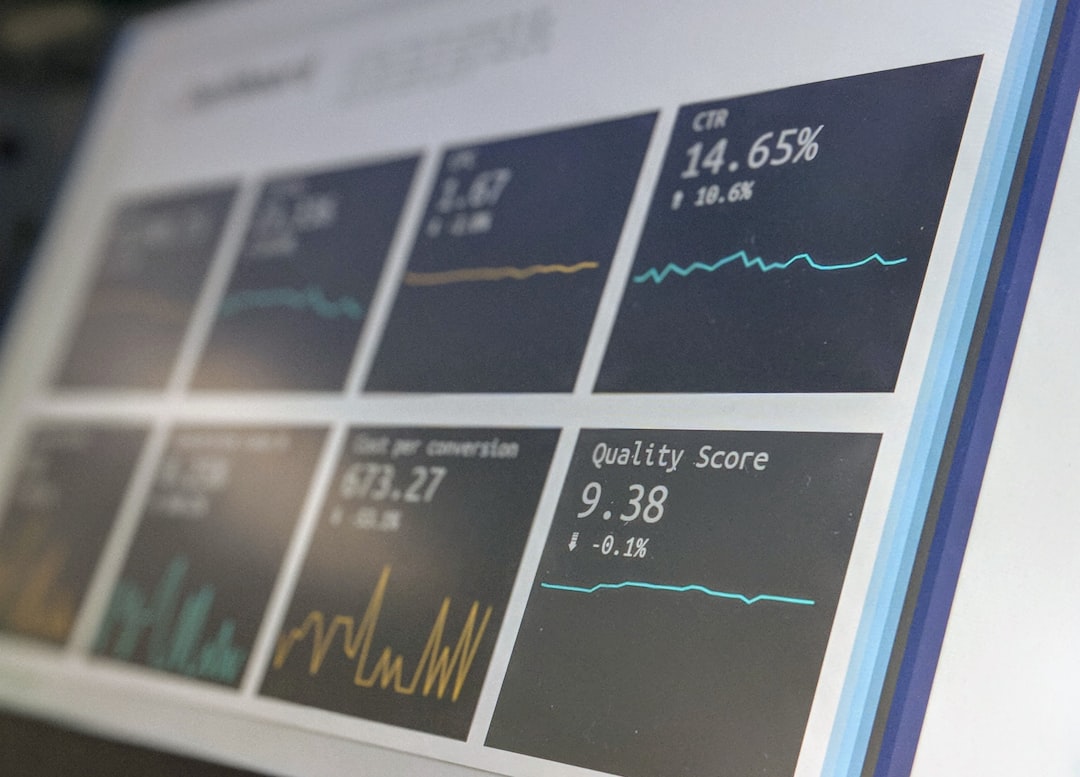
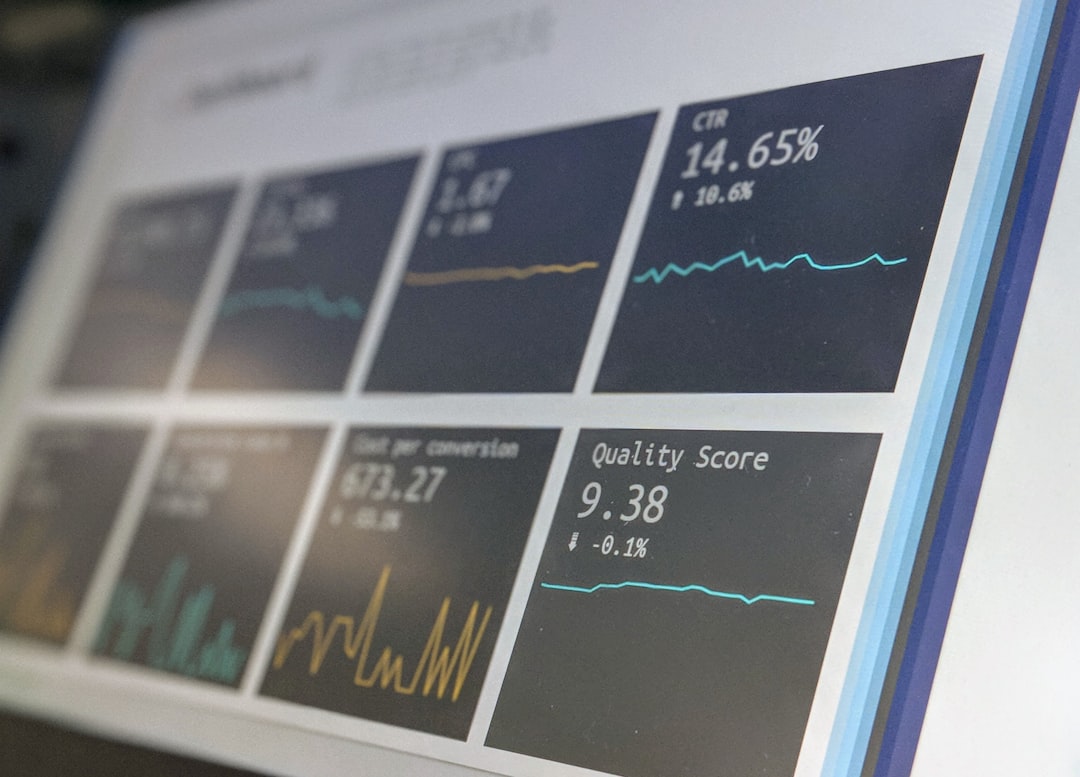
# Introduction. As we step into 2023, economists, analysts, and businesses alike are seeking to understand the myriad of factors that could influence the economy over the next few years. With the lingering effects of the global pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and significant shifts in consumer behavior, economic predictions remain crucial for navigating an uncertain future. In this post, we'll explore key trends that could shape the economic landscape, providing insights into volumes of data and expert opinions to help you prepare for what lies ahead. # Analyzing Current Economic Indicators. To make informed predictions about the economy, it is essential to analyze current economic indicators such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation rates, unemployment figures, and consumer confidence. According to recent data, many countries have shown signs of a slow recovery from recession, albeit with bumpy progress. GDP growth rates in major economies like the United States, China, and the Eurozone have experienced a moderate uptick, while inflation remains a significant concern due to supply chain disruptions and energy price fluctuations. Tracking these indicators closely provides a practical map of where we might be headed economically. # Inflation: A Persisting Concern. Inflation has become a keyword for 2023 discussions, as central banks grapple with the challenge of rising prices. Commodity prices have surged, impacting everything from fuel to food costs. As a response, monetary policy is undergoing scrutiny. The Federal Reserve, for example, is carefully navigating its interest rate strategy. An increase in interest rates could cool inflation but may also slow economic growth. Predictions suggest that while inflation pressures may taper, challenges remain in managing consumer expectations and supply-side constraints impacting various industries. # Labor Market Dynamics. In addition to inflation, shifts in the labor market are creating a complex environment for economic predictions in 2023. Emerging trends include hybrid work models and the increasing demand for skilled labor in technology and healthcare. As companies adapt to these changes, workforce shortages may continue to affect productivity gains in different sectors. Additionally, rising wages in response to labor demand complicate inflation trajectories. Experts predict that the labor market will stabilize over the next two years, but not without challenges in workforce adaptability and training. # Global Trade and Geopolitical Influences. Another critical aspect to consider is global trade dynamics and geopolitical tensions. Controversies surrounding tariffs, trade agreements, and supply chain dependencies will influence economic forecasts. For instance, the ongoing tension between major economies may exacerbate trade barriers, further impacting inflation and the availability of goods. Insights into these geopolitical factors suggest a trend towards regionalization or diversification in supply chains, which could alter international trade flows significantly. # Consumer Behavior and Economic Sentiment. Consumer behavior plays a fundamental role in economic predictions. After the pandemic, consumer preferences shifted, with a greater focus on sustainability and digital services. In 2023, businesses that effectively reach out to environmentally conscious customers will likely thrive. Moreover, changes in spending habits can drive economic momentum or create downturns depending on consumers' confidence levels. Surveys indicate a mixed sentiment among consumers, and businesses need to navigate these shifts to stay attuned to market demands. # Technology's Role in Economic Evolution. The acceleration of technology adoption during the pandemic has reshaped industries and consumer experiences. Digital transformation is not only critical for businesses to survive but also for economic vibrancy. Predictions for 2023 highlight the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation as game-changers for enhancing productivity. Investments in technology could lead to the creation of new jobs, but also raise questions about workforce displacement and the need for reskilling initiatives. # Conclusion. As we look beyond 2023, a multifaceted landscape of economic predictions emerges characterized by inflationary pressures, shifting labor dynamics, and technological advancements. While the economy shows signs of recovery, it is crucial for stakeholders to remain vigilant and adaptable amid uncertainties. Monitoring key indicators and understanding the underlying trends could provide a clearer picture of the coming years. Preparing for possible scenarios—whether of economic growth or downturn—will be essential for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike. .