Best Practices for Data Visualization in Economics
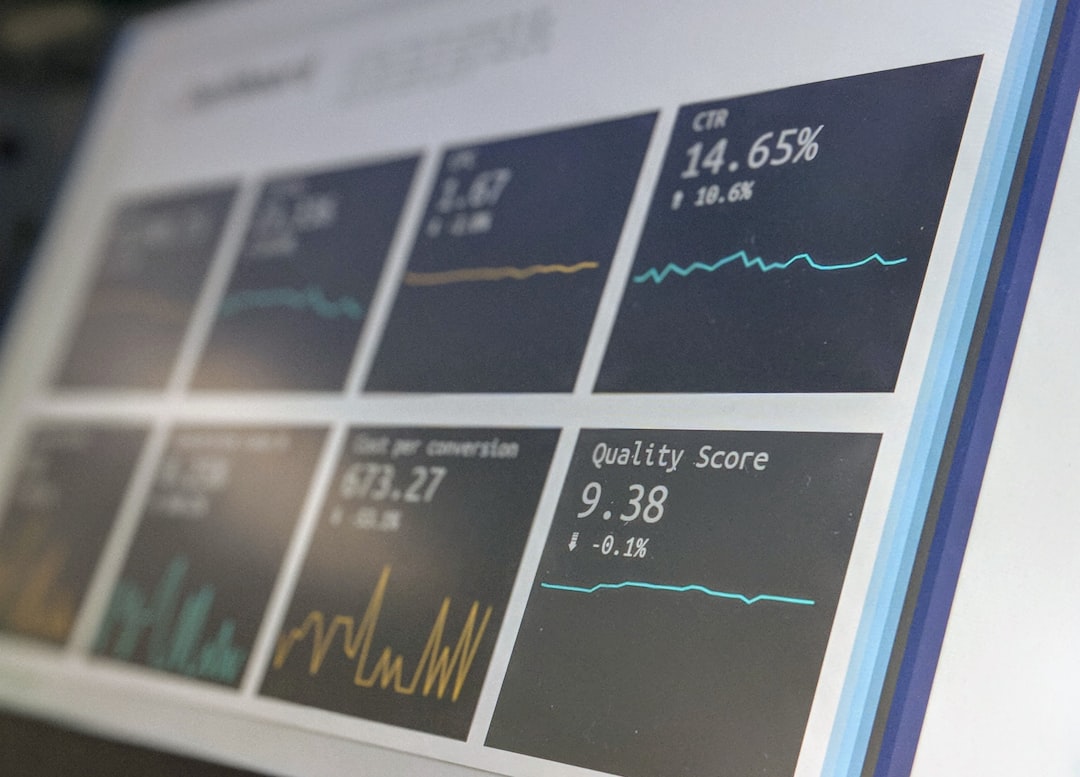
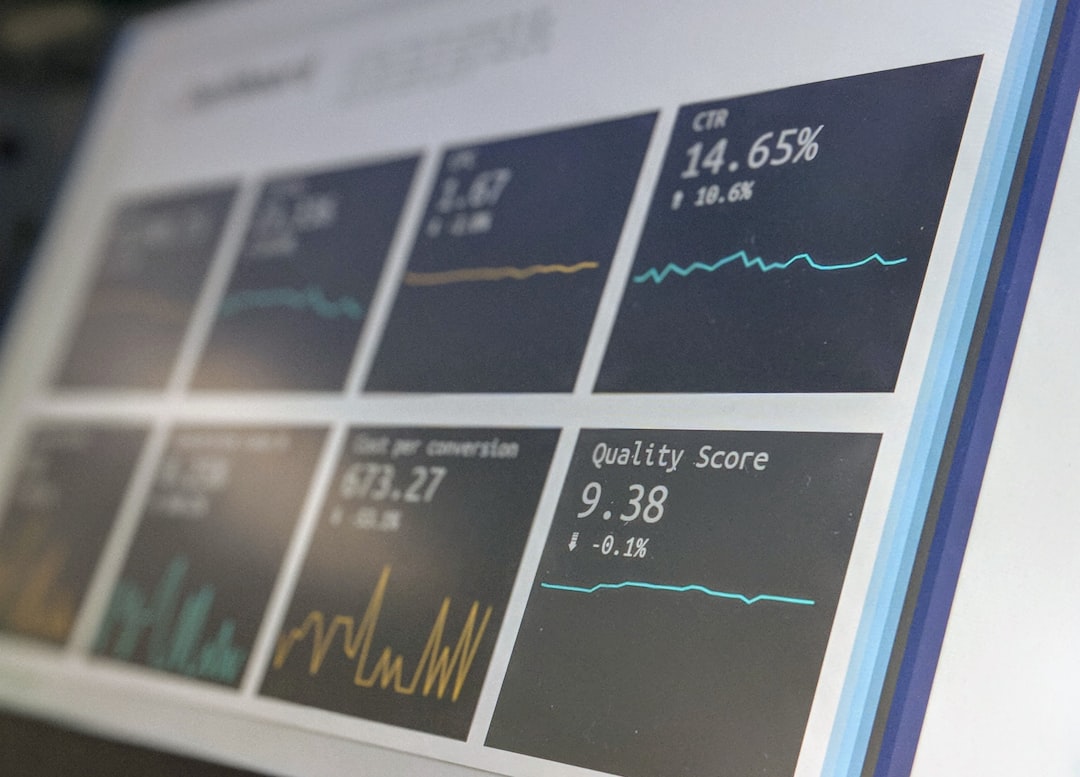
# Introduction. In today's data-driven world, the ability to communicate information clearly and effectively is paramount, especially in fields like economics where complex data is at the forefront of analysis. Data visualization serves as a crucial tool for economists and business professionals seeking to present their findings in a compelling and understandable way. In this blog post, we will explore best practices for data visualization in economics, discussing how to effectively convey patterns and insights through visuals while avoiding common pitfalls. # Understanding Your Audience. Before diving into data visualization, it's essential to identify your audience and understand their knowledge base and expectations. Economists often present their findings to policymakers, business leaders, or the general public, all of whom have different levels of expertise. This understanding should influence your choice of data visualization types, colors, and even the complexity of the information presented. For example, when targeting policymakers, you might adopt a more straightforward visualization approach focusing on key indicators to drive actionable insights. Tailoring your visuals to suit your audience enhances comprehension and engagement. # Choosing the Right Type of Visualization. With a myriad of data visualization types available, selecting the right one is critical in effectively conveying your message. Common visualization methods include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, heat maps, and scatter plots, each serving different purposes. For instance, line graphs are excellent for illustrating trends over time, while bar charts can compare different categories. Understanding the specific attributes of your dataset will guide you in choosing the most appropriate type of visualization. Avoid overcomplicating visuals; prioritize clarity and simplicity to keep your audience focused on the analysis. # Color Usage and Design Principles. The visual appeal of your data presentation significantly impacts audience engagement. Color plays a vital role in data visualization, as it can highlight important data points, categorize information, and elicit emotional responses. However, overusing colors or relying on them alone can lead to confusion. Aim for a color palette that is accessible to everyone, including those with color blindness. Stick to a maximum of five colors to avoid overwhelming viewers and ensure enough contrast between background and foreground elements to enhance readability. Additionally, consistent sizing and spacing between elements create a clean and organized layout. # Labeling and Annotation. Proper labeling of axes, data points, and legends is fundamental to effective data visualization. Ensure all components are clearly labeled so the audience can easily discern the message you’re conveying. In addition, annotations can provide context or explanations for specific data points, guiding viewers through your analysis. Using concise and comprehensive titles can also help communicate what the visual represents, establishing clear expectations. Remember, less is more; avoid cluttering your visuals with unnecessary data or excessive text. # Avoiding Misleading Statistics. One of the most significant risks in data visualization is presenting data in a way that can be misconstrued. Be mindful of scale manipulation that can distort interpretations — for example, starting a graph at a non-zero point to exaggerate trends. Use precise and complete datasets, as selective data representation can lead to biased narratives. Transparency in data sources and methodologies used in analysis is essential to retain credibility and trust, particularly in economic reporting. # Testing and Feedback. Before finalizing your data visualizations, seek feedback from colleagues or target audience members. Testing presents an opportunity to catch potential misunderstandings or design flaws early on. Gathering input can help refine content, ensuring it achieves the desired communicative effect effectively. Incorporating constructive criticism will only enhance the quality of your visuals and increase their impact in conveying economic data. # Conclusion. Data visualization has transformed the landscape of data presentation in economics, making complex information accessible and engaging. By adhering to best practices, economists and business professionals can enhance communication through effective visual storytelling. Focusing on audience understanding, choosing appropriate visualization types, utilizing color thoughtfully, and maintaining transparency are key steps in crafting compelling data visualizations. As you continue to refine your data visualization skills, strive to balance sophistication with clarity — the result will be powerful insights that resonate with your audience. .