How to Leverage Open Data for Economic Research
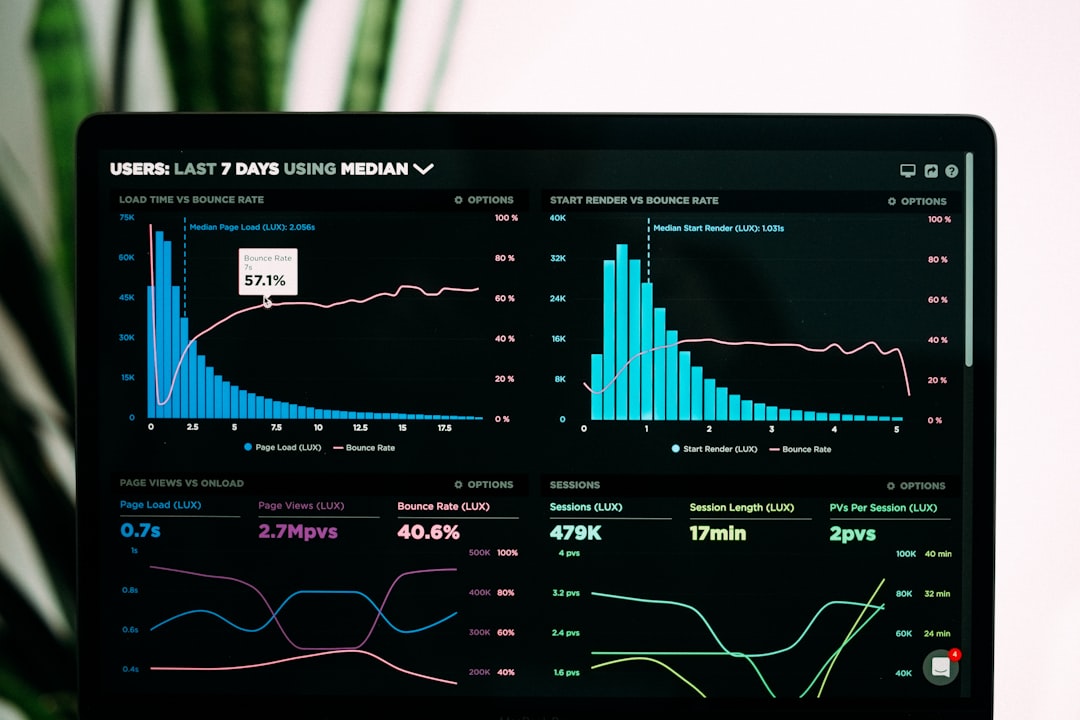
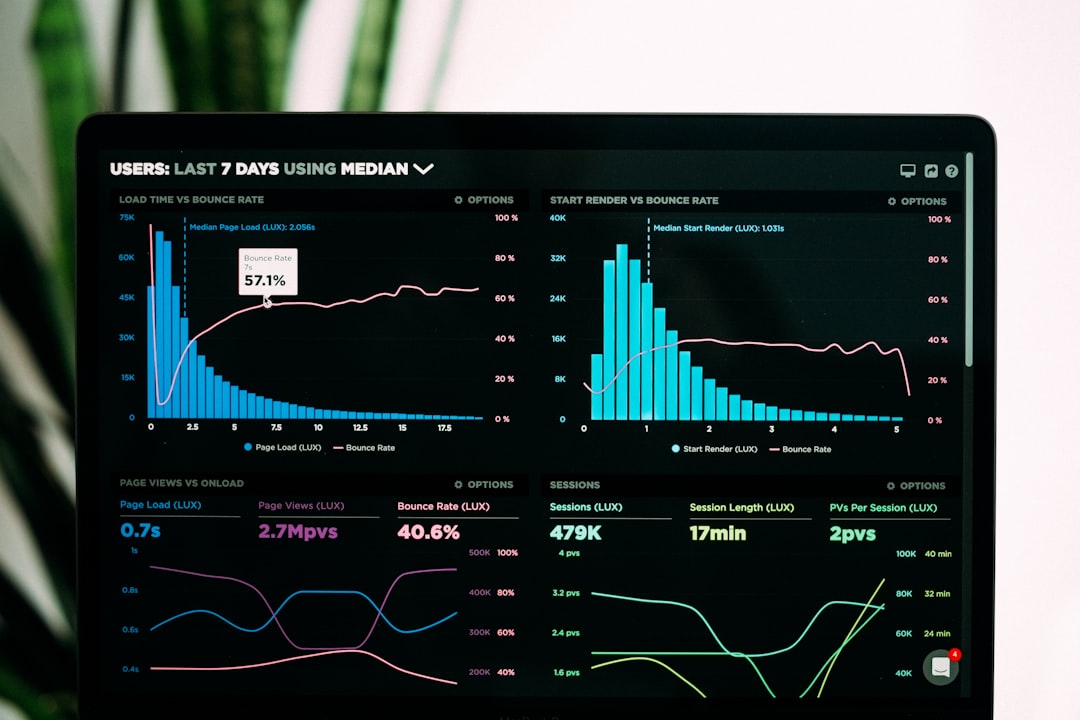
# Introduction. In an era where data is often referred to as the new oil, understanding how to effectively leverage open data for economic research is more crucial than ever. Open data—publicly available datasets that anyone can access, use, and share—can dramatically enhance the scope and quality of economic studies. It offers researchers, policymakers, and analysts deeper insights into economic trends, demographic shifts, and resource allocations. This guide will delve into effective methods and best practices for utilizing open data to drive meaningful economic analysis. # Understanding Open Data. Open data is a concept that revolves around the availability of data to the public with minimal restrictions. It ranges from local government statistics like unemployment rates to global datasets on trade flows or environmental impacts. Central to its effectiveness in economic research is the idea that the more accessible data is, the more innovative and productive usage can be derived from it. This openness signifies transparency and can lead to improved governance, accountability, and citizen engagement. Researchers can analyze trends and patterns by tapping into vast resources of data across various sectors. However, understanding the types of data and their sources is crucial for effective utilization. # Sources of Open Data. When considering how to leverage open data, identifying reliable sources is critical. Many governments and international organizations provide datasets for public use, including: 1. **Government Portals**: Local, state, and federal governments often have open data portals (like data.gov in the United States) that provide accessible datasets relevant to economic indicators, demographics, and geographic information. 2. **International Organizations**: Institutions like the World Bank, IMF, and OECD regularly publish reports and datasets that can facilitate cross-country comparisons and research. 3. **Academic Institutions**: Many universities produce open datasets through studies or research projects, which can be invaluable for niche economic research. 4. **NGOs and Think Tanks**: Organizations focused on economics often collect and publish data on various socio-economic issues. Their datasets can be rich in insights and useful for data analysis. # Analyzing Data for Insights. Once you have access to the data, the next step involves analysis. Here are some recommended methods: 1. **Statistical Analysis**: Using statistical tools and software (such as R or Python) can help you uncover trends and patterns in the data. Applying techniques like regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and time-series analysis can yield valuable insights into economic relationships. 2. **Data Visualization**: Tools like Tableau or Power BI allow you to create visual representations of your data, making complex information more digestible. Showing data trends through graphs or interactive dashboards can enhance presentations to stakeholders or in publications. 3. **Comparative Studies**: By comparing datasets across regions or timeframes, researchers can identify shifts in economic patterns, making it easier to infer causal relationships. This approach can provide actionable insights for policymakers. # Overcoming Challenges. While open data offers substantial benefits, researchers must navigate several challenges: 1. **Data Quality**: Open datasets can often vary in accuracy and completeness. Identifying the credibility and accuracy of the data source is essential before relying on its insights. 2. **Data Compatibility**: Datasets from different sources may use varying formats or terminologies. Researchers must often clean and standardize data to ensure it can be effectively analyzed together. 3. **Ethical Use**: Understanding how to use open data ethically is vital. Researchers must adhere to guidelines regarding privacy and consent, particularly when dealing with sensitive information. # Utilizing Findings Effectively. After conducting thorough analyses and deriving insights from open data, the next step is effectively communicating these findings. This can be done through: 1. **Publishing Reports**: Making the findings available in comprehensive reports can help disseminate knowledge among stakeholders, ensuring that insights can influence economic policy and practice effectively. 2. **Engagement with Stakeholders**: Presenting findings to relevant stakeholders—including government bodies, other researchers, and the public—can increase transparency and stimulate discussions on potential applications of the insights gained. 3. **Feedback and Iteration**: Engaging with the community and stakeholders can garner feedback that fosters iterative improvements to future research. It can lead to more refined methodologies and more precise conclusions moving forward. # Conclusion. In conclusion, leveraging open data can significantly enrich economic research and analysis. Through effective sourcing, rigorous analysis, and clear communication of findings, researchers can use open data to unveil deeper economic insights, thus fostering transparency and informed decision-making. As the realm of open data continues to grow, embracing this resource will only become more essential for analysts and policymakers alike. # Recommended Resources. - Data.gov for American datasets. - The World Bank for global development data. - Various academic institutions for sector-specific datasets. - Tools like R, Python, Tableau for data analysis and visualization. .