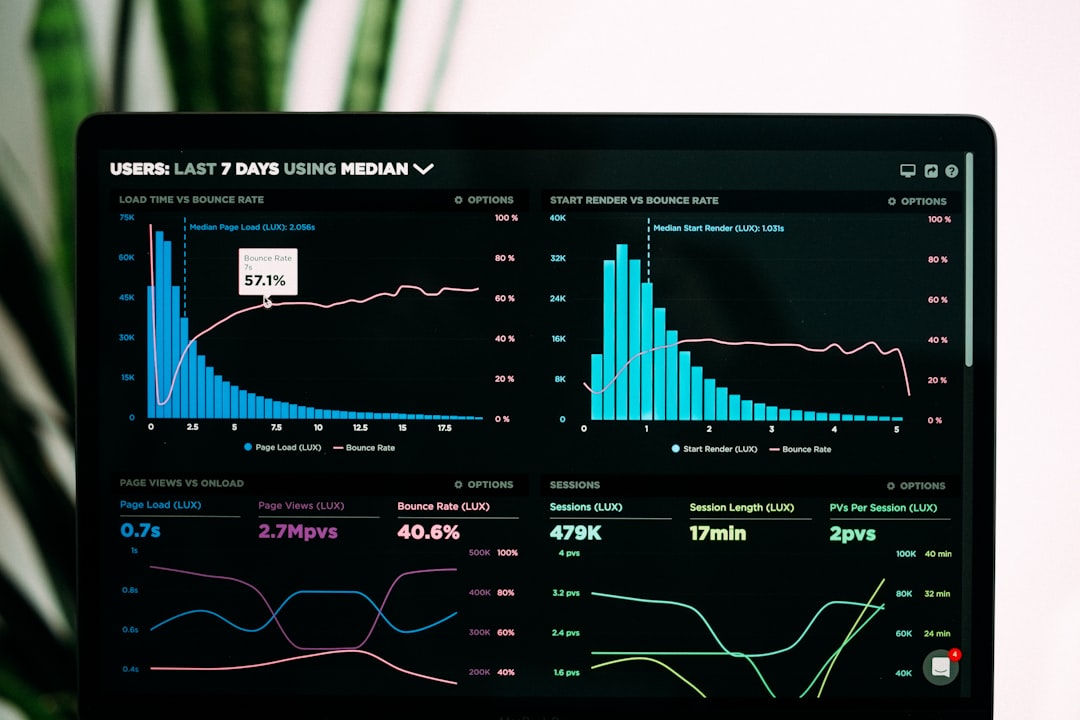
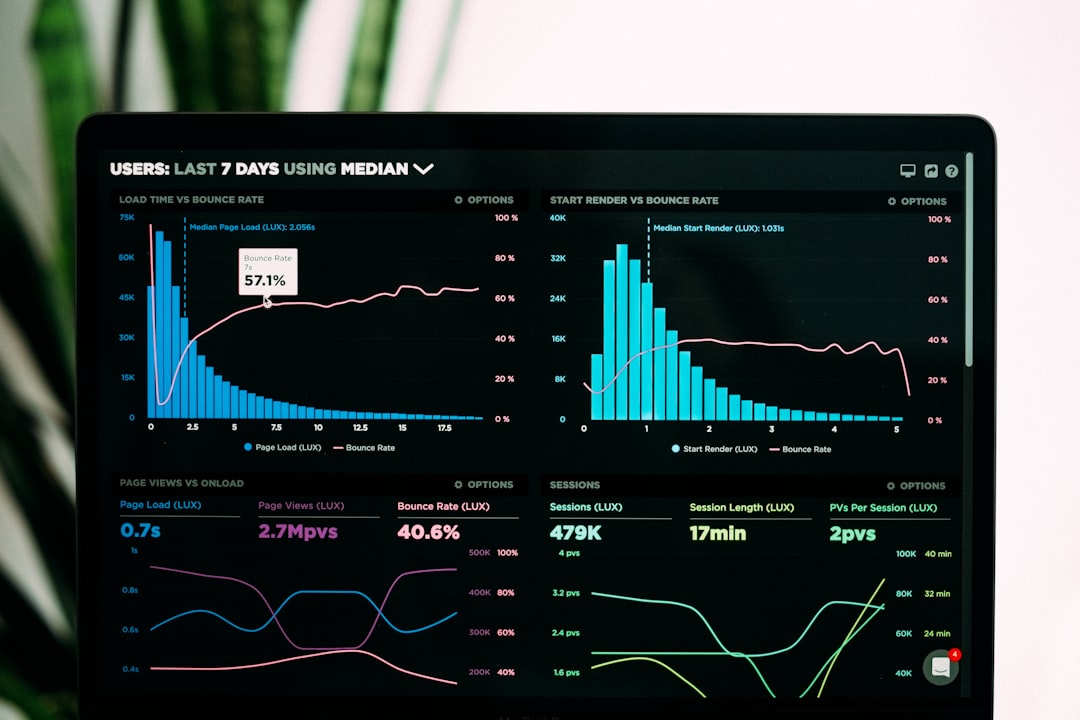
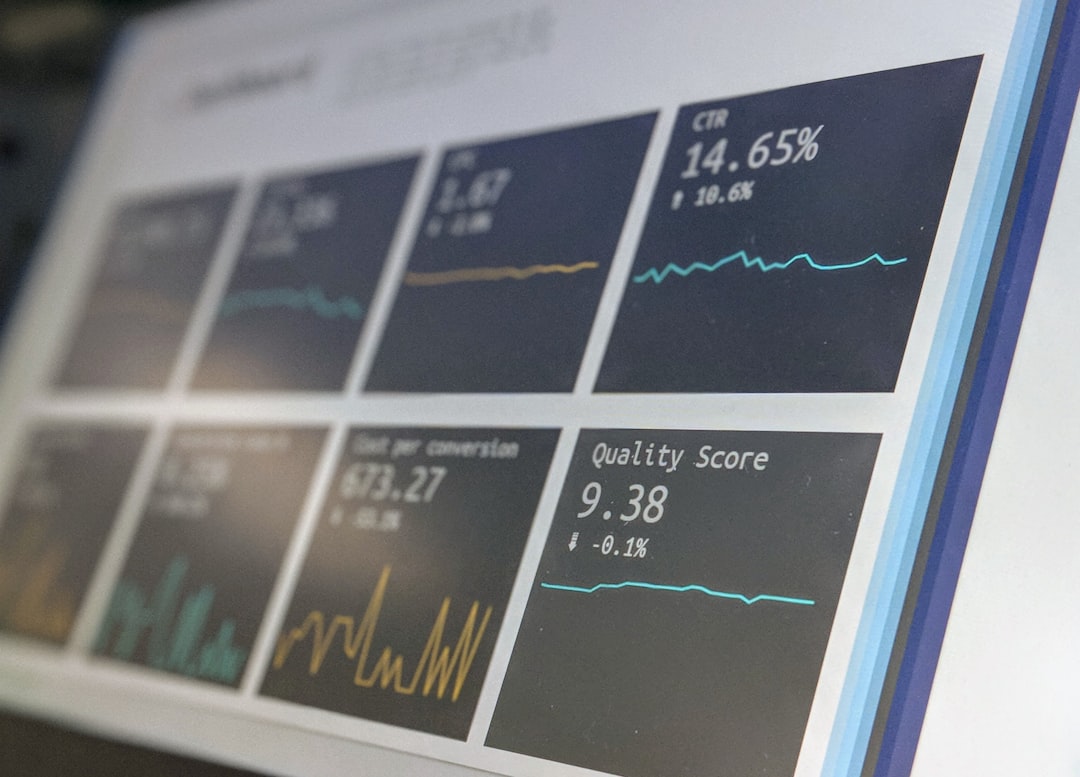
Economic Resources for Entrepreneurs: A Comprehensive Guide
# Introduction. Entrepreneurship is a vibrant and challenging pathway that requires a blend of creativity, tenacity, and financial acumen. Economic resources are fundamental for entrepreneurs looking to kickstart or expand their ventures. However, navigating through the myriad of options available can be daunting. In this guide, we'll explore essential economic resources that can bolster entrepreneurial efforts and offer insights into effective strategies to leverage these resources. # Understanding Economic Resources. Economic resources encompass all the tangible and intangible assets that entrepreneurs utilize to create goods and services. These resources include financial capital, human resources, physical assets, and intellectual properties. Understanding how to acquire, manage, and optimize these resources can be the difference between success and failure in the entrepreneurial landscape. ### Financial Capital. One of the most critical economic resources for any entrepreneur is financial capital. Whether it's for starting a new business or growing an existing one, access to funds is crucial. Entrepreneurs can tap into various sources, including: 1. **Personal Savings:** Many entrepreneurs begin their journey by investing personal savings. This familiar resource allows for greater control but also increases personal financial risk. 2. **Investors:** Attracting investors, whether angel investors or venture capitalists, can provide substantial funding. Having a solid business plan and clear vision is essential for drawing in potential investors. 3. **Loans and Grants:** Traditional bank loans, government assistance programs, and grants from private foundations can be a lifeline. Entrepreneurs should be prepared with a detailed proposal and financial projections to apply successfully. ### Human Resources. The ability to attract and retain talented individuals is another crucial aspect of economic resources. Entrepreneurs should focus on: 1. **Networking:** Building a professional network can help in finding potential team members, mentors, and advisors. Local business meetups, industry conferences, and social media platforms like LinkedIn are excellent starting points. 2. **Training and Development:** Invest in continuous learning for your team. Programs that enhance skills can improve productivity and job satisfaction, ultimately benefiting the business in the long run. 3. **Diversity and Inclusion:** A diverse team brings various perspectives, which can drive innovation and creativity. Embracing inclusion should be a priority for modern entrepreneurs. ### Physical Assets. While virtual businesses thrive in the digital age, physical assets remain invaluable, particularly for service-oriented or retail businesses. Key considerations include: 1. **Location:** The right location can significantly impact a business. High foot traffic areas can lead to increased sales for retail, while a strategic remote setup might work better for online businesses. 2. **Equipment:** Procuring necessary equipment—whether computers for a digital startup or machinery for a production line—is vital. Entrepreneurs should evaluate their options between buying and leasing to make financially sound choices. 3. **Inventory Management:** Effective management of inventory is essential for minimizing costs and maximizing revenue. Implementing an inventory management system can streamline operations, helping entrepreneurs to focus on growth. ### Intellectual Property. Intellectual property (IP) can be the lifeblood of innovation-driven businesses. Protecting and leveraging IP assures competitive advantage and can create new revenue streams. Entrepreneurs should consider: 1. **Registration:** Patents, trademarks, and copyrights should be registered to safeguard unique products, brand names, or processes. 2. **Licensing:** Entrepreneurs can also generate income through licensing agreements, allowing others to use their patented technologies or branded products. 3. **Trade Secrets:** Maintaining confidentiality around processes or formulas can give businesses a market edge and should be a part of strategic planning. ### Building a Support System. Economic resources can also extend beyond tangible assets. A robust support system consisting of mentors, business incubators, and community organizations can have a profound impact: 1. **Mentorship Programs:** Engaging with seasoned entrepreneurs can provide guidance and shortcuts to success, making the journey less overwhelming. 2. **Community Support:** Local entrepreneurs can band together to form cooperative networks that provide resources, share best practices, and create a sense of community. 3. **Online Communities:** Digital forums, such as business-related groups on Facebook or Reddit, allow for sharing experiences and resources, broadening your entrepreneurial reach. # Conclusion. In conclusion, understanding and leveraging economic resources is paramount for the success of any entrepreneur. By diversifying funding sources, investing in human resources, optimizing physical assets, safeguarding intellectual property, and building a supportive network, entrepreneurs can set themselves on a path to success. Embrace the journey, continue learning, and adapt to the ever-changing economic landscape. .