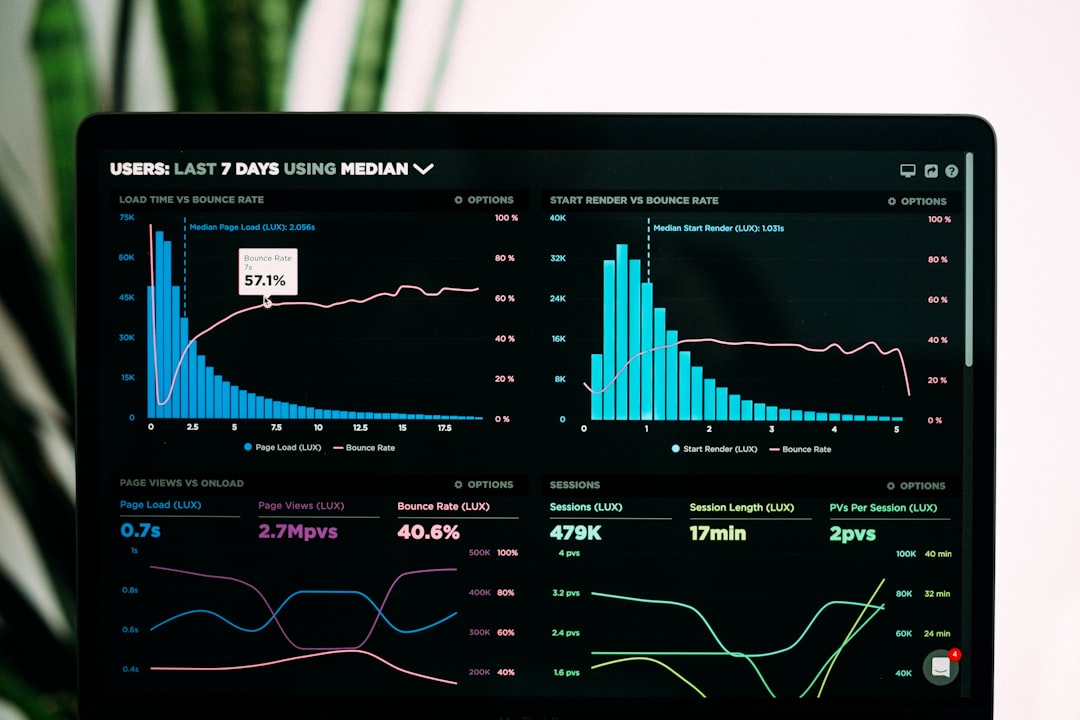
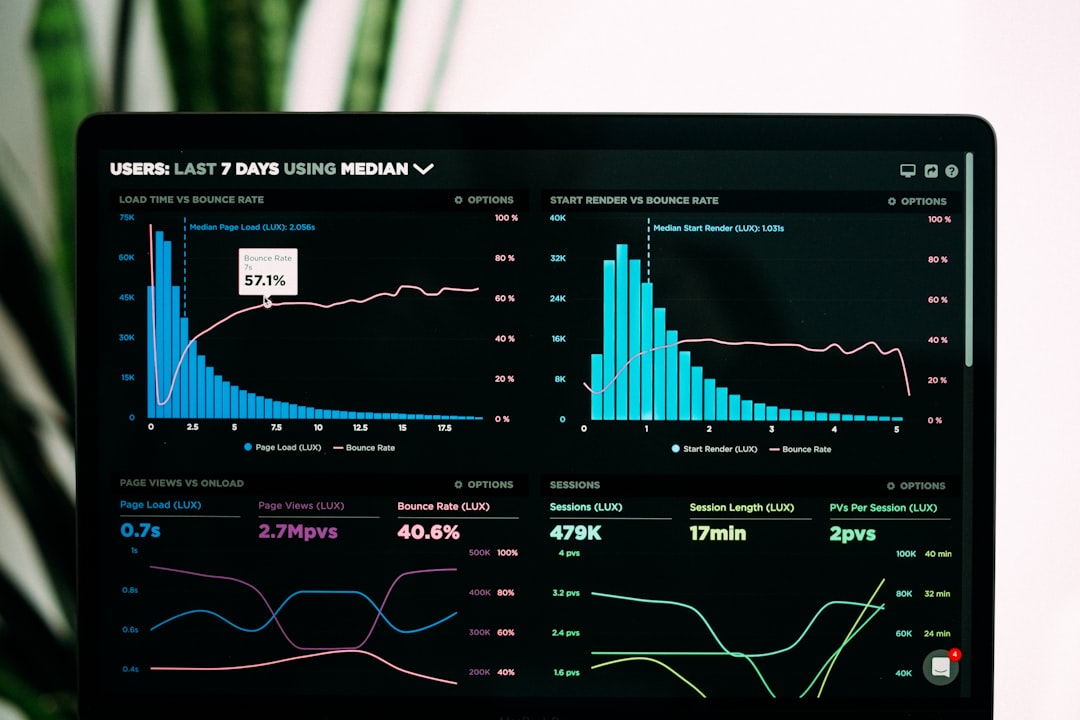
Guide to Economic Impact Assessments: Understanding the Basics and Best Practices
# Introduction. Economic impact assessments (EIAs) are critical tools used by governments, organizations, and businesses to evaluate the effects of policies, projects, or programs on the economy. Given the complexities of our global economy, understanding the utility and execution of these assessments is essential for stakeholders involved in economic planning and development. This guide seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of economic impact assessments, covering what they are, why they matter, and how they can be effectively conducted. # What is an Economic Impact Assessment?. At its core, an economic impact assessment measures the direct and indirect effects of a project, policy, or event on the economy. This might include changes in employment, government revenue, industry production, and consumer spending. EIAs typically focus on the regional or national levels and aim to provide quantitative and qualitative insights that can help guide decision-making. The need for EIAs can arise in various scenarios such as the introduction of new regulations, the development of infrastructure projects, or even changes in tax policy. By reflecting not only the monetary value of changes, EIAs allow stakeholders to understand broader societal impacts that might arise from economic shifts. # Why Economic Impact Assessments Matter?. Economic impact assessments serve several critical purposes. First, they provide a platform for transparent decision-making by presenting evidence-based conclusions regarding the implications of economic changes. Organizations and governments can use these assessments to justify actions, influence public policy, or garner support from stakeholders. Moreover, EIAs are instrumental in identifying potential risks and benefits associated with projects. For example, in the case of a proposed highway construction, an EIA can reveal how the construction might promote regional development while also indicating potential adverse effects such as increased traffic and pollution. Finally, EIAs can assist in planning for future development by forecasting potential outcomes based on current economic conditions and trends. This can ultimately lead to smarter, more sustainable economic policies. # The Process of Conducting an Economic Impact Assessment. Conducting an EIA involves several essential steps. The first step is defining the scope and objectives of the assessment. This involves identifying the specific project or policy that will be evaluated, the stakeholders involved, and the metrics that will be used to gauge economic impact. The next step is data collection, where quantitative data (such as surveys and economic data) and qualitative data (such as interviews and case studies) are gathered. It’s crucial to use reliable data sources to ensure the validity of the assessment results. Once data collection is complete, analysts employ various methodologies to assess economic impacts, using models such as input-output models or econometric models that can capture both direct and indirect effects. After analysis, the final step involves drafting the assessment report, where findings are presented alongside recommendations for stakeholders. # Common Methodologies Used in Economic Impact Assessments. Different methodologies may be more appropriate depending on the context of the assessment. Input-output analysis is one of the most frequently used methodologies, as it outlines how different sectors of the economy interrelate. However, it may not capture all dynamics of modern economies. Cost-benefit analysis is another common approach, measuring the net costs versus the benefits of a project or policy. This is useful in determining the overall value of a specific endeavor. Additionally, econometric modeling can predict future impacts based on historical data, providing valuable insights into potential changes driven by specific initiatives. # Challenges in Economic Impact Assessments. While economic impact assessments are invaluable tools, they do face several challenges. One significant issue is data availability and accuracy; not having access to reliable data can lead to flawed assessments. Moreover, the assumptions made during the modeling process can significantly affect outcomes, and different analysts may come to different conclusions based on the methods they apply. In addition, the complexity of economic interactions can lead to difficulties in isolating specific impacts. For instance, discerning whether a job created is a result of a public investment or general economic growth can be challenging. These challenges underline the importance of thoroughness and transparency throughout the assessment process. # Conclusion. Economic impact assessments are important instruments that help stakeholders navigate the complex landscape of economic policy and development. By understanding the goals, methodologies, and challenges associated with EIAs, organizations, and governments can make more informed decisions that ultimately foster economic growth while mitigating negative impacts. Whether for planning an infrastructure project or evaluating policy changes, effective EIAs can improve community outcomes and enhance overall economic health. Legitimate and detailed assessments lay the groundwork for sustainable economic development and create avenues for future opportunities in various sectors. As stakeholders continue to navigate an ever-changing economy, the value of comprehensive economic impact assessments cannot be overstated. .