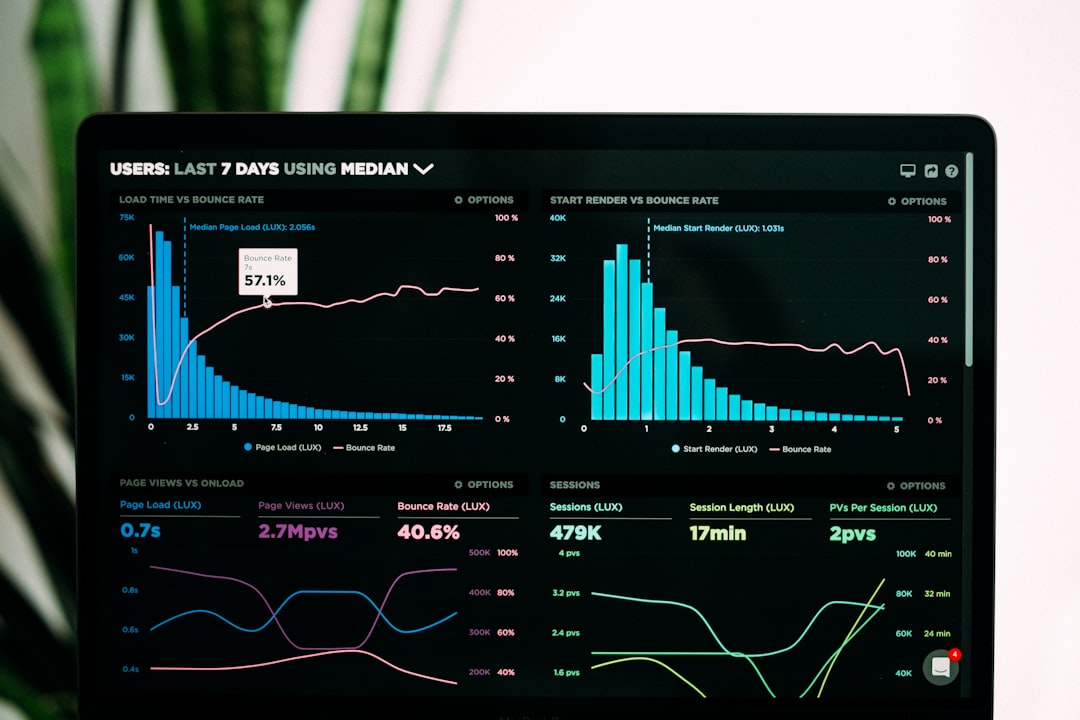
Guide to Economic Impact Assessments: Understanding the Fundamentals.
## Introduction. Economic impact assessments (EIAs) are critical tools used by businesses, governments, and organizations to evaluate the potential economic effects of a project, policy, or investment. These assessments provide valuable insights into how changes in economic activity can affect various stakeholders, from local businesses to employment levels and tax revenues. In this blog post, we will explore the basics of economic impact assessments, the methodologies used, and the importance of accurate assessment in decision-making processes. ## Importance of Economic Impact Assessments. In the modern economy, the ability to predict the economic outcomes of investments, policy changes, or development projects is essential. EIAs not only assist in understanding the potential benefits but also help identify possible adverse effects. For instance, a thorough assessment can highlight how a new factory may create jobs and stimulate local businesses while also providing an analysis of environmental impacts or community disruptions. By conducting EIAs, stakeholders can make informed decisions that balance economic growth with social and environmental responsibility. ## Key Components of an Economic Impact Assessment. An effective economic impact assessment typically consists of several key components. 1. **Project Overview:** Understanding the project, including its scope, financial requirements, and expected outcomes, is fundamental. 2. **Target Area Analysis:** Assessing the geographical area affected by the project, including local demographics, existing economic conditions, and employment patterns. 3. **Data Collection:** Gathering quantitative and qualitative data relevant to the project is crucial. This may involve historical economic data, surveys, and interviews with community members or business leaders. 4. **Economic Modeling:** Utilizing economic models such as input-output models, econometric models, or computable general equilibrium (CGE) models to analyze the potential impacts on local and regional economies. 5. **Impact Evaluation:** Understanding the direct, indirect, and induced effects of the project on employment, output, income, and taxes. 6. **Reporting and Recommendations:** Summarizing findings in a clear and accessible manner that informs stakeholders and includes actionable recommendations. ## Methodologies Used in EIAs. There are various methodologies employed for conducting economic impact assessments, each suited for different types of projects and objectives. 1. **Input-Output Analysis:** This quantitative method focuses on the relationships between industries and measures how changes in one industry affect others. 2. **Cost-Benefit Analysis:** This method compares the benefits of a proposed action or investment to its costs, providing a straightforward metric for decision-making. 3. **Regional Economic Models:** These models evaluate impacts on a specific geographic area and often incorporate local population, resources, and infrastructures into their calculations. 4. **Surveys and Interviews:** Qualitative assessments can be formed through engaging with local businesses, residents, and stakeholders to gather insights that numerical data alone may not capture. ## Challenges in Conducting Economic Impact Assessments. While EIAs can provide invaluable insights, several challenges may arise during the assessment process. - **Data Availability and Quality:** Access to reliable data can be limited, particularly in rural or underdeveloped areas. - **Defining Boundaries:** Determining the geographic and economic boundaries for assessment can complicate the analysis and findings. - **Uncertainty in Predictions:** Predictions about economic impacts involve a degree of uncertainty, and unexpected factors can significantly influence results. - **Stakeholder Engagement:** It's crucial to have the support and input of relevant stakeholders to ensure a comprehensive assessment. However, achieving consensus can be difficult. ## The Role of Technology in Economic Impact Assessments. The rise of technology has transformed how economic impact assessments are conducted. Software tools and data analytics platforms now allow for more efficient data collection, modeling, and reporting. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can visualize data geographically, while advanced analytical methods like machine learning enhance predictive capabilities. These technologies not only streamline the assessment process but also improve accuracy and accessibility of findings. ## Conclusion. Economic impact assessments are essential for informing decision-makers about the potential outcomes of new projects or policies. By providing a comprehensive look at the anticipated economic effects, EIAs help ensure that investments align with community needs and promote sustainable growth. As the landscape of economics and technology continues to evolve, refining EIA methodologies and embracing new tools will enable more robust and meaningful assessments. Effective economic impact assessments are not just about numbers; they are about understanding the broader implications of economic decisions in real people's lives. .